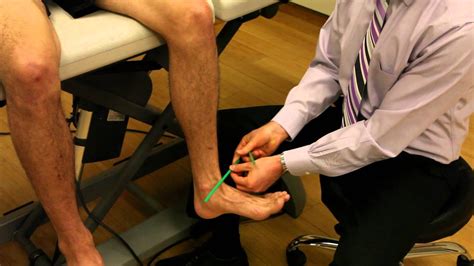
tibial torsion test sitting|how to assess tibial torsion : distribute Tibial torsion is inward twisting of the tibia (shinbone) and is the most common cause of in-toeing. It is usually seen at age 2 years. Males and females are affected equally, . Resultado da 2 dias atrás · Bosch brings together comprehensive expertise in vehicle technology with hardware, software, and services to offer complete mobility solutions. Discover the entire portfolio Industry and trades
{plog:ftitle_list}
Para conhecer os conteúdos oficias do Fatal Model, clique aqui. . Jacobina - BA Mulheres Homens Trans Ana Julia Offline há 1 hora Atendimento 24 horas R$ 250/h 34 anos Com local 1 review Centro, Jacobina - BA Amanda Cedraz Offline há 6 dias Atendimento em Hotéis R$ 200/h
Dr. Rome explains the proper technique to determine if a patient exhibits any degree of external tibial torsion.Special thank you to Dr. Matthew Rome and Equ.
Internal Tibial Torsion is a common condition in children less than age 4 which typically presents with internal rotation of the tibia and an in-toeing gait. Diagnosis is made clinically with a thigh-foot angle > 10 degrees of .
tibial torsion special test
tibial torsion in adults
Title: Tibial Torsion Test---SittingSource: Orthopedic Physical Assessment, 7th Edition.Author: David J. Magee, BPT, PhD, CM and Robert C. Manske, PT, DPT, S. Dr. Rome explains how to look for tibial torsion, or tibial rotation, with the knee at a 90 degree angle. Tibial torsion is inward twisting of the tibia (shinbone) and is the most common cause of in-toeing. It is usually seen at age 2 years. Males and females are affected equally, .Tibial torsion is the twisting of a child’s shinbone, also known as the tibia. In most cases, tibial torsion causes a toddler’s legs and feet to turn inward (internal tibial torsion), giving them a pigeon-toed appearance. Less often, the legs turn .
Tibial torsion can be assessed by comparing the bimalleolar axis with the position of the tibial tubercle. Note the foot shape: Metatarsus adductus may be the primary cause of in-toeing, particularly in the infant.Tibial torsion is diagnosed (and distinguished from other causes of in-toeing) by a careful physical exam. Tibial torsion is assessed by measuring the thigh-foot angle, if the foot is shaped normally.Thigh-foot angle (TFA): a means to measure tibial torsion. To measure internal or external tibial torsion, the patient is positioned in prone lying with their knees flexed to 90° and foot resting in its natural position. The TFA is measured .Craig's test is a passive test that is used to measure femoral anteversion or forward torsion of the femoral neck. . Pediatric orthopedic mythbusters: the truth about flexible flatfeet, tibial and femoral torsion, W-sitting, and idiopathic toe .
Tibial torsion test in sitting position; Too many toes sign; Purpose of the special tests: These tests are used to check the tibial torsion of the leg. It is also checked the toe position. Tibial torsion test in the prone position: The .Craig's test is a passive test that is used to measure femoral anteversion or forward torsion of the femoral neck. It is also known as 'Trochanteric Prominence Angle Test (TPAT)'. Femoral anteversion is the angle between the femoral neck and femoral shaft, indicating the degree of torsion of the femur. It is also known as Femoral neck anteversion. trochanteric prominence angle test . . tibial torsion. look at thigh-foot angle in prone position. normal value in infants- mean 5° internal (range, −30° to +20°) . sitting restrictions do not change natural history. Operative. derotational femoral osteotomy. indications < 10° of external rotation on exam in an older child (>10 yrs)
GENERAL INFORMATION. Active movements of the lower leg, ankle, and foot should be done in both weight-bearing and non-weight-bearing positions (long leg sitting or supine lying), and the examiner should note any differences, because foot deformities and deviations, in addition to decreased range of motion (ROM), can lead to injury in other parts of .Tibial Torsion What is tibial torsion in children? Tibial torsion is an inward twisting of the shinbones. These bones are located between the knee and the ankle. Tibial torsion causes a child’s feet to turn inward. . Know why a test or procedure . Out-toeing is caused by external tibial torsion and femoral retroversion. Angular problems include genu varum (bowleg) and genu valgum (knock knee). . Sitting habits: the W sitting position is .
Internal tibial torsion is commonly associated with sitting on the feet, while increased femoral anteversion is associated with sitting in a “W” position. Aggravating factors Torsional .Tibial torsion can be external (lateral) or internal (medial). (See also Introduction to Congenital Craniofacial and Musculoskeletal Disorders.) External tibial torsion occurs normally with growth: from 0 ° at birth to 20 ° by adulthood. External torsion is rarely a problem. Internal tibial torsion is common at birth, but it typically .Tibial torsion is an inward twisting of the shinbones. These bones are located between the knee and the ankle. Tibial torsion causes a child's feet to turn inward. . Know what to expect if your child does not take the medicine or have the test or procedure. If your child has a follow-up appointment, write down the date, time, and purpose for . Tibial torsion can be assessed by comparing the bimalleolar axis with the position of the tibial tubercle. Note the foot shape: Metatarsus adductus may be the primary cause of in-toeing, particularly in the infant.
physical therapy for tibial torsion
Rigid Forefoot Valgus - This foot prematurely converts to propulsion at a time when it should still be absorbing shock. Symptoms include a tendency to ankle sprains, an unsure gait, every foot pain imaginable, leg muscle problems, stress fractures, etc. Orthotic treatment includes an orthotic that tricks the forefoot into thinking all the bones are level with each other by bringing . Tibial torsion was calculated by subtracting the proximal tibial angle from the distal tibial angle. . The accuracy of a test can be defined as how close a measured value is to a true value. In this case it means, how close the clinical measurement of tibial torsion is to the real torsion measured by CT or in a cadaver. . Tibial torsion is defined as any twisting of the tibia on its longitudinal axis which produces a change in the alignment of the planes of motion of the proximal and distal articulations ().It undergoes structural remodelling, which begins in utero and progresses throughout childhood and adolescence to skeletal maturity ().The prevalence of rotational pathology of the femur . Physical exam test procedure for examination of the foot and ankle and associated structures.
May Lead to Hamstring Tightness, Tibial Torsion and Hip Dislocation; In a W-sitting position, the hips are placed at the extreme limits of internal rotation, predisposing the child to future orthopedic problems. In this abnormal position, . Normally, lateral rotation of the tibia increases from approximately 5º at birth to approximately 15º at maturity; femoral anteversion decreases from approximately 40º at birth to approximately 15º at maturity. Tibial torsion Tibial torsion is inward twisting of the tibia (shinbone) and is the most common cause of intoeing.
Internal tibial torsion is most frequently bilateral, and may at times present with metatarsus adductus, femoral anteversion, or physiologic bow legging. Pertinent clinical findings on examination include a forward or outward-facing patella, or in a seated position, there may be a posterior rotation of the medial malleolus (in comparison to the .
True tibial (tibiofibular) torsion involves lateral axial change and occurs as a part of normal development (changes in Japanese children with respect to sitting postures; Yagi 1994). While estimates of the proportions vary, there is uniformity in observations of intoeing gait, which support this as a normally decreasing finding with age (see .Rotational deformity is a less common cause of patellar instability than trochlear dysplasia and patella alta. In some cases, rotational deformity is the primary bony factor producing the instability and should be corrected surgically. More research is needed on what are normal values for femoral version and tibial torsion, as well as when the axial plane alignment needs to be . Try this quick test to determine if you are lacking Tibial Internal Rotation. a) Test For Tibial Internal Rotation. Instructions: Sit down on a chair. Make sure that your knee is bent at 90 degrees. Keep your knee pointing forwards at all times. Turn your shin bone inwards without moving the knee.This may be due to the position your child was sitting in while in the uterus. Intoeing due to internal tibial torsion is generally most noticeable when a child begins walking. . For severe tibial torsion that does not improve by 8 to 10 years old and causes the child difficulty with walking or sports, surgery may be recommended. .
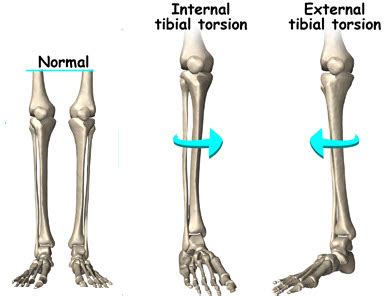
Children with femoral anteversion often prefer the "W" sitting position because it is more comfortable. This should not be discouraged or avoided. . Internal tibial torsion causes an in-toeing gait from a twisting of the tibia (shin bone). It is most often first noticed when a child is first starting to walk, and is most common between the .Tibial torsion is an inward twisting of the shin bones (the bones that are located between the knee and the ankle). Tibial torsion causes the child's feet to turn inward, or have what is also known as a "pigeon-toed" appearance. It is typically seen among toddlers. What causes tibial torsion? Tibial torsion can occur due to the position of the .Tibial torsion is the turning of a child’s lower leg (tibia) either inward (internal tibial torsion) or outward (external tibial torsion). The condition often improves without treatment, usually before a child turns 4. Some children with tibial torsion wear a night brace between 18 to 30 months old, but this is not common.
In East Asian countries with a floor-sitting culture, . Statistical analysis was performed using the Friedman test (v.8.0c; GraphPad Software, La Jolla, CA, USA) for the TMA and for changes over time following treatment initiation. . The tibial torsion transformer is applied with the knee joint in flexion and is designed so that the .
internal tibial torsion in adults
Tibial torsion can happen because of the position of the baby in the uterus. It also tends to run in families. Typically, a child’s walking style looks like that of their parents. What are the symptoms of tibial torsion in a child? . Know why a test or procedure is .
how to measure tibial torsion
how to correct tibial torsion
how to assess tibial torsion
webJulia is a high-level, high-performance dynamic language for technical computing. The main homepage for Julia can be found at julialang.org. This is the GitHub repository of Julia source code, including instructions for compiling and installing Julia, below.
tibial torsion test sitting|how to assess tibial torsion